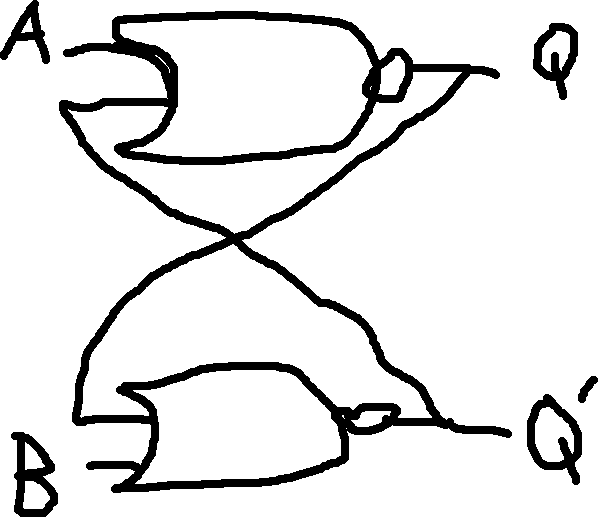
Latch: Sequential circuit that watches all inputs continuously and changes its outputs at any time independently of a clocking signal.
SR-Latch (Reset-Set Latch): Use two inputs and two outputs.
On Q’: Exists mainly for manufacturers. Not present in dynamic memory.
The simplest SR Latch can be made with two NOR gates wired together like so:
| A (R) | B (S) | Q | Q’ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | MEMORY | MEMORY |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
When S=R=0, the circuit acts as a memory cell and keeps its previous state.
Note: We don’t like it when R=S=1, because it creates a Q=Q' relationship, so some books will say this is not permitted.
On Tracing: Look for inputs that tell you the result in one-shot, e.g.,
- if a NOR gate gets
1, it must output0- if a NAND gets a
0, it must output1- et cetera.
Used to capture (latch) the logic level present on the Data line.
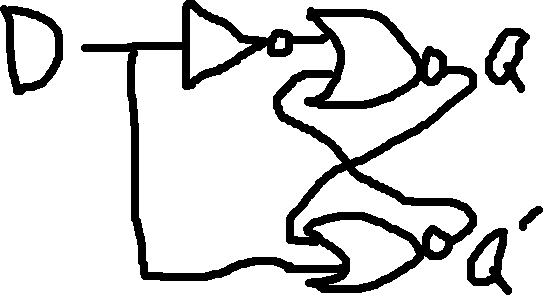
| D | Q | Q’ |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
If the circuit uses a clock, we call it a flip-flop, otherwise it is a switch.
High v.s. Low Level: A high-level flip flop only responds to input when the clock is a high voltage, a low-level flip flop only responds when it’s low voltage.
High Level Triggered RS-Flip Flop:
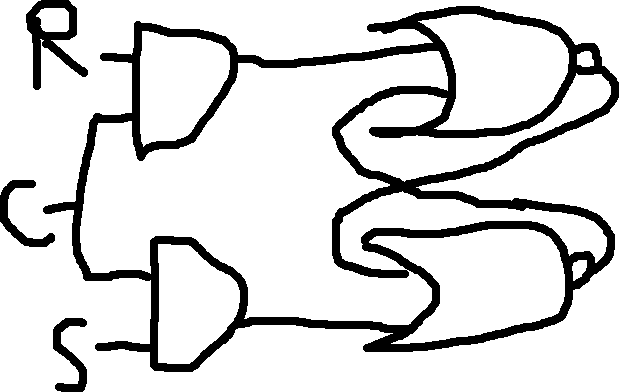
| R | S | C | Q | Q’ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | MEMORY | MEMORY |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | MEMORY | MEMORY |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | MEMORY | MEMORY |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | MEMORY | MEMORY |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | MEMORY | MEMORY |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
Low Level Triggered RS-Flip Flop:
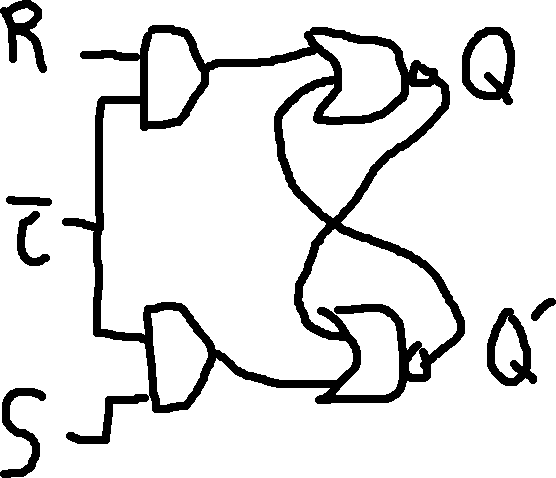
| R | S | C | Q | Q’ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | MEMORY | MEMORY |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | MEMORY | MEMORY |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | MEMORY | MEMORY |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | MEMORY | MEMORY |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | MEMORY | MEMORY |
High Level Triggered D-Flip Flop:
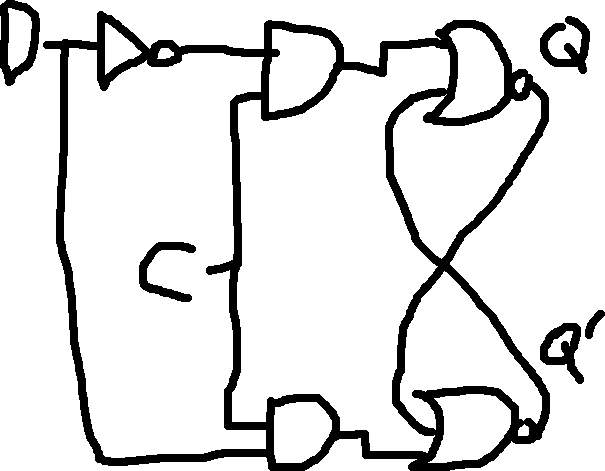
| D | C | Q | Q’ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | MEMORY | MEMORY |
| 1 | 0 | MEMORY | MEMORY |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
Low Level Triggered D-Flip Flop:
| D | C | Q | Q’ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | MEMORY | MEMORY |
| 1 | 1 | MEMORY | MEMORY |
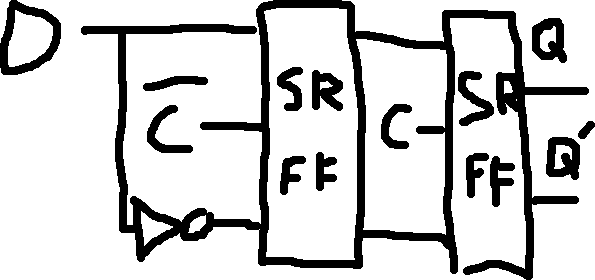
Rising v.s. Falling Edge Triggered: Triggers on the edge of the clock pulse (when it’s going from 0 \to 1 (rising) or 1 \to 0 (falling)).
Rising Edge Triggered SR Flip Flop:
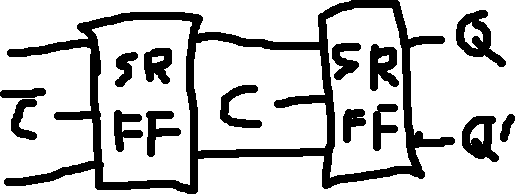
Falling Edge Triggered SR Flip Flop:
Rising Edge Triggered D Flip Flop:
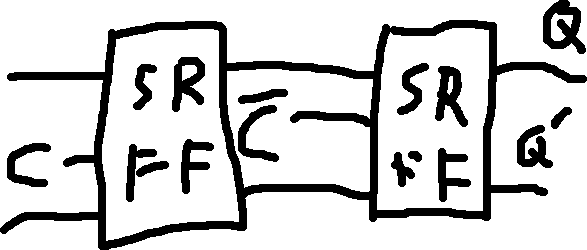
Falling Edge Triggered D Flip Flop:
If T=0, Q will be toggled. If T=0, Q will be memory.
| T | Q | Q’ |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | MEMORY | MEMORY |
| 1 | Q’ | Q |
T flip-flops aren’t manufactured in the real world, we just use JK flip-flops.
“JK doesn’t stand for Jack-Kilby” — The professor
Operates on sequential logic, output depends not only on current inputs, but the previous state as well.
| J | K | C | Q | Q’ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | X | 0 | MEMORY | MEMORY |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | MEMORY | MEMORY |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | Q’ | Q |